Understanding the Prostate: Essential Knowledge for Men
As I sat down to write about preventing prostate-related illnesses, memories of my grandfather’s health struggles came flooding back. He battled with prostate issues in his later years, prompting me to delve deeper into understanding how these conditions can be prevented.
With each piece of research I uncovered, I felt a sense of urgency to share this knowledge with others, to empower them to take control of their own prostate health. It became clear to me that simple lifestyle changes could make a significant difference in reducing the risk of prostate-related illnesses.
Understanding the Prostate:
Essential Knowledge for Men
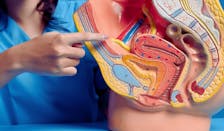
The prostate gland is a small, walnut-sized organ located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. While it may be small in size, its role in men's health is significant. Understanding the prostate and its functions is essential for men of all ages. Here's what you need to know:
Anatomy and Function
The prostate gland plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system.
It produces fluid that nourishes and protects sperm, helping them survive longer in the female reproductive tract.
During ejaculation, muscles in the prostate gland help propel semen into the urethra and out of the body.
Common Prostate Conditions
Prostate Cancer: Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men after skin cancer. It occurs when cells in the prostate gland grow out of control. Early detection through regular screening is key for successful treatment.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. It can cause urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, and weak urine flow.
Prostatitis: Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland, often caused by infection. Symptoms may include pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, difficulty urinating, and fever.
Risk Factors
Age: The risk of developing prostate conditions increases with age. Prostate cancer is rare in men under 40 but becomes more common as men get older.
Family History: Men with a family history of prostate cancer are at higher risk. Having a father or brother with prostate cancer doubles a man's risk of developing the disease.
Ethnicity: African American men have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer compared to men of other ethnicities. They are also more likely to develop prostate cancer at a younger age and have a more aggressive form of the disease.
Prevention and Screening
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and regular exercise may help reduce the risk of prostate conditions.
Screening: Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood tests and digital rectal exams (DRE) are used for prostate cancer screening. Talk to your healthcare provider about when to start screening and how often to be tested based on your individual risk factors.
Treatment Options
Treatment for prostate conditions depends on the specific diagnosis and severity of symptoms.
Prostate Cancer: Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these approaches.
BPH: Treatment options for BPH include medication to relax the muscles of the prostate gland or reduce its size, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery in severe cases.
Prostatitis: Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial prostatitis. Pain relievers and alpha-blockers may also help relieve symptoms.
Maintaining Prostate Health
Stay Informed: Educate yourself about prostate health and be proactive about screening and preventive measures.
Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your prostate health and address any concerns.
Open Communication: Discuss any changes or symptoms you may be experiencing with your healthcare provider promptly.
In conclusion, understanding the prostate and taking proactive steps to maintain prostate health is crucial for men's overall well-being. By staying informed, knowing the risk factors, and seeking appropriate medical care when needed, men can take control of their prostate health and reduce the risk of developing serious conditions.
© 2024 DailyHealthJournal.net | All Rights Reserved
This site is not a part of Google™ website or network of sites such as Youtube™ or any company owned by Google™ or Youtube™. Additionally this website is not endorsed by Google™ Youtube™ Inc. in any way. Google™ is a trademark for all their respective companies.

Understanding the Prostate:
Essential Knowledge for Men
As I sat down to write about preventing prostate-related illnesses, memories of my grandfather’s health struggles came flooding back. He battled with prostate issues in his later years, prompting me to delve deeper into understanding how these conditions can be prevented.
With each piece of research I uncovered, I felt a sense of urgency to share this knowledge with others, to empower them to take control of their own prostate health.
It became clear to me that simple lifestyle changes could make a significant difference in reducing the risk of prostate-related illnesses.
And so, fueled by a desire to help others safeguard their well-being, I embarked on a journey to compile evidence-based strategies for prevention into a comprehensive guide.
Understanding the Prostate:
Essential Knowledge for Men
The prostate gland is a small, walnut-sized organ located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. While it may be small in size, its role in men's health is significant. Understanding the prostate and its functions is essential for men of all ages. Here's what you need to know:
Anatomy and Function
The prostate gland plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system.
It produces fluid that nourishes and protects sperm, helping them survive longer in the female reproductive tract.
During ejaculation, muscles in the prostate gland help propel semen into the urethra and out of the body.
Common Prostate Conditions
Prostate Cancer: Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men after skin cancer. It occurs when cells in the prostate gland grow out of control. Early detection through regular screening is key for successful treatment.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. It can cause urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, and weak urine flow.
Prostatitis: Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland, often caused by infection. Symptoms may include pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, difficulty urinating, and fever.
Risk Factors
Age: The risk of developing prostate conditions increases with age. Prostate cancer is rare in men under 40 but becomes more common as men get older.
Family History: Men with a family history of prostate cancer are at higher risk. Having a father or brother with prostate cancer doubles a man's risk of developing the disease.
Ethnicity: African American men have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer compared to men of other ethnicities. They are also more likely to develop prostate cancer at a younger age and have a more aggressive form of the disease.
Prevention and Screening
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and regular exercise may help reduce the risk of prostate conditions.
Screening: Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood tests and digital rectal exams (DRE) are used for prostate cancer screening. Talk to your healthcare provider about when to start screening and how often to be tested based on your individual risk factors.
Treatment Options
Treatment for prostate conditions depends on the specific diagnosis and severity of symptoms.
Prostate Cancer: Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these approaches.
BPH: Treatment options for BPH include medication to relax the muscles of the prostate gland or reduce its size, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery in severe cases.
Prostatitis: Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial prostatitis. Pain relievers and alpha-blockers may also help relieve symptoms.
Maintaining Prostate Health
Stay Informed: Educate yourself about prostate health and be proactive about screening and preventive measures.
Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your prostate health and address any concerns.
Open Communication: Discuss any changes or symptoms you may be experiencing with your healthcare provider promptly.
In conclusion, understanding the prostate and taking proactive steps to maintain prostate health is crucial for men's overall well-being. By staying informed, knowing the risk factors, and seeking appropriate medical care when needed, men can take control of their prostate health and reduce the risk of developing serious conditions.
© 2024 DailyHealthJournal.net | All Rights Reserved
This site is not a part of Google™ website or network of sites
such as Youtube™ or any company owned by Google™
or Youtube™. Additionally this website is not endorsed
by Google™ Youtube™ Inc. in any way. Google™ is a
trademark for all their respective companies.

And so, fueled by a desire to help others safeguard their well-being, I embarked on a journey to compile evidence-based strategies for prevention into a comprehensive guide.